
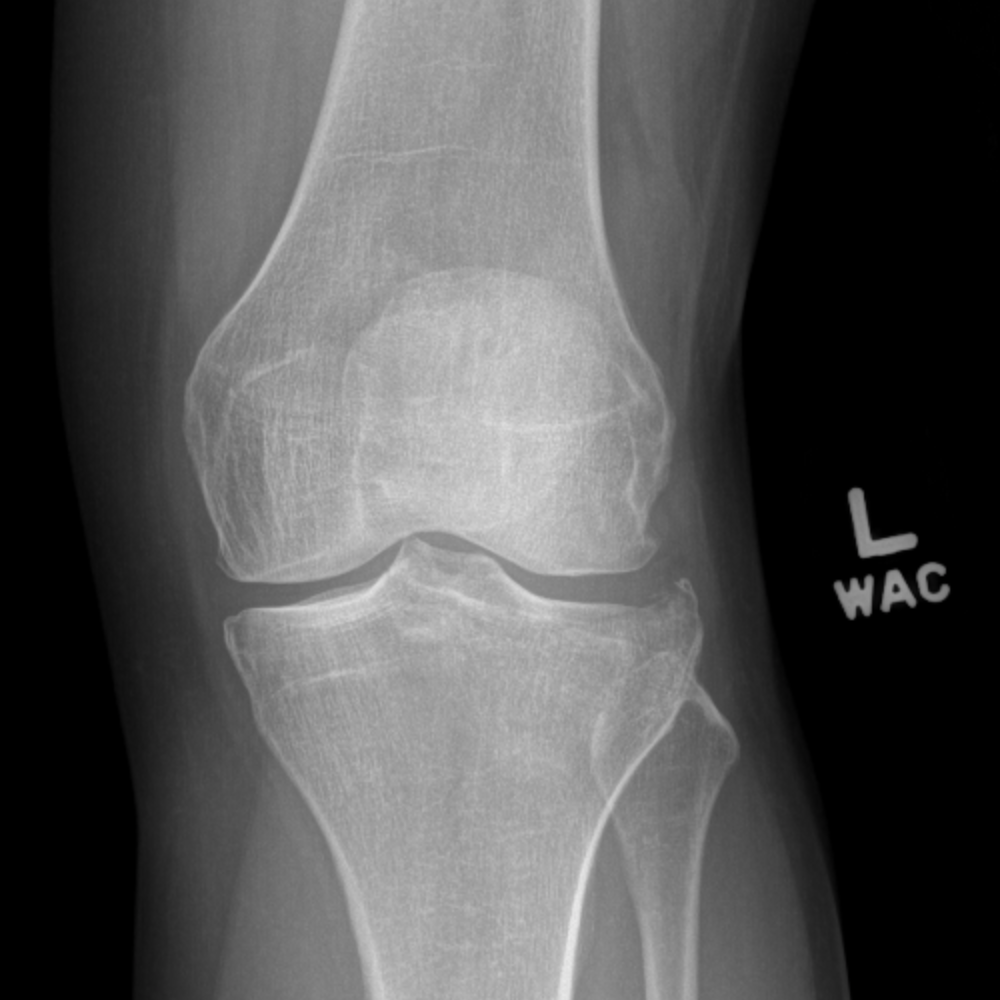
#TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE SKIN#
Inspect the skin circumferentially in order not to miss an open fracture. Social history – it’s important to know the pre-injury functional status and occupation of the patient, as well as smoking status. Past medical history – specifically ask about diabetes and peripheral vascular disease. These are commonly high-energy injuries – have a low threshold for an ATLS assessment and trauma call.Īlways perform an initial assessment for compartment syndrome, an open fracture and neurovascular status.ĭocument time and mechanism of injury in as much detail as you can – whether the fracture has occurred with a jumping injury, a twisting mechanism, or direct trauma (dashboard injury/contact sports) has implications on the likely associated soft tissue injuries.Īsk about pain elsewhere (distracting injury).Īsk about any sensory changes in the leg. Left to right: tibial plateau, shaft and pilon fractures Initial assessment The general principles of initial assessment and management are similar for all tibial fractures, so these will be dealt with together, with differences between the injuries highlighted where appropriate. As such, it is vital to consider neurovascular injury, soft tissue compromise and compartment syndrome in all tibial fractures. These fractures often result from high energy mechanisms, such as road traffic accidents (although they may also occur following low energy trauma, especially in those with osteoporotic bone). These injuries may coexist: it is relatively common to have a shaft fracture with intra-articular extension, or even separate fractures of the proximal/distal tibia and the shaft. Of note, the latter are distinct to ankle fractures, which do not involve the weight-bearing portion of the distal tibia (the plafond). In broad terms, fractures may be divided into those affecting the proximal tibial articular surface (tibial plateau fractures), extra-articular fractures of the shaft, and those affecting the distal articular surface (pilon fractures). The tibia is the most commonly fractured long bone. Admission, discharge and calling a senior


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
